Basic and History of Linux
Navigating the Foundations and Evolution: Exploring the Basics and Evolutionary Journey of Linux
In the vast landscape of modern computing, Linux stands as a pillar of innovation, collaboration, and adaptability. As an open-source operating system, Linux has not only revolutionized the technology industry but has also paved the way for a new era of computing possibilities. This article delves into the evolution, diversity, and impact of Linux on the world of computing.
Evolution of Linux:
Linux, created by Linus Torvalds in 1991, was born from a desire to build a free and open-source alternative to proprietary operating systems. Its foundation lies in the Unix-like structure, allowing for scalability, stability, and security. Over the years, Linux has seen remarkable growth, attracting developers and enthusiasts worldwide.
Impact on Modern Computing:
Linux has transcended its origins and found its way into everyday life. It powers smartphones, smart TVs, supercomputers, and more. Android, the world's most popular mobile operating system, is based on the Linux kernel. Additionally, technologies like containerization (Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes) heavily rely on Linux for their functioning.
Linux:
Linux is kernel not OS
Linux is not a UNIX derivative. It was written from scratch
A Linux distribution is the Linux kernel and a collection of software that together creates an OS.
Linux Features:
Open source
Secure
Simplified updates for all installed software
Light weight
Multi-User or Multi-Task
Multiple distributions – RedHat, Debian, Fedora etc.
File System Hierarchy:
/home - home directory for other user/root – It is home directory for root user/boot – It contains bootable files for Linux/etc - It contains all configurations files./usr – By default software are installed in this directory/bin – It contains commands used by all users/sbin - It contains commands used by only root user/opt – Optional application software Packages/dev – Essentials device files. This includes terminal devices, usb or any devices attached to the system.
Linux Commands & It’s use cases:
cat command – The cat command is one of the most universal tools, yet all it does is Copy standard input to Standard Output.

Touch Command-


Vi editor:
A programmer text editor
It can be used to edit all kinds of plain text, it is specially useful for editing programs, mainly used for Unix programs.
Notes:- :w – to save, :wq or :x – To save and quit, :q – quit, :q! – force quit(no save)
- Vi is a standard whereas ‘nano’ has to be available depending on the linux we use.
rmdir – This command is used to remove the specified directory (empty)rmdir -p – Removes both the parent and child directoryrmdir -pv – Removes all the parent and sub-directories along with verbose.rm -rf – Removes even non-empty file and directory.Rm -rp – Removes non-empty directories including parent and sub directory.rm -r – Removes empty directoryhostnameIfconfig, cat /etc/os-releaseyum install httpdyum remove httpdyum update httpdservice httpd startservice httpd statuschkconfig httpd onchkconfig httpd offwhichwhoamiechoyum list intalleduseradd- To create usergroupadd – To create a groupgpasswd -a/-m – To add user into group, to add multiple userln – Hardlink/ backupln -s – Softlink/ short cuttar – Tar is an archiver used to combine multiple files into onegzip – It is a compression tool used to reduce the size of a filewget – It is the non-intracity network downloader.
Access mode/ Permission:
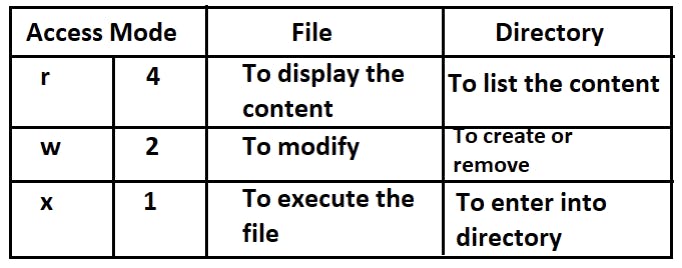
chmod – Used to change the access modechown – Change the owner of the file or directorychgrp – Change the group of file or directory
File Details:

Note: r = read, w = write, x \= execute
rm -rf * - To remove all file/directory in single command
